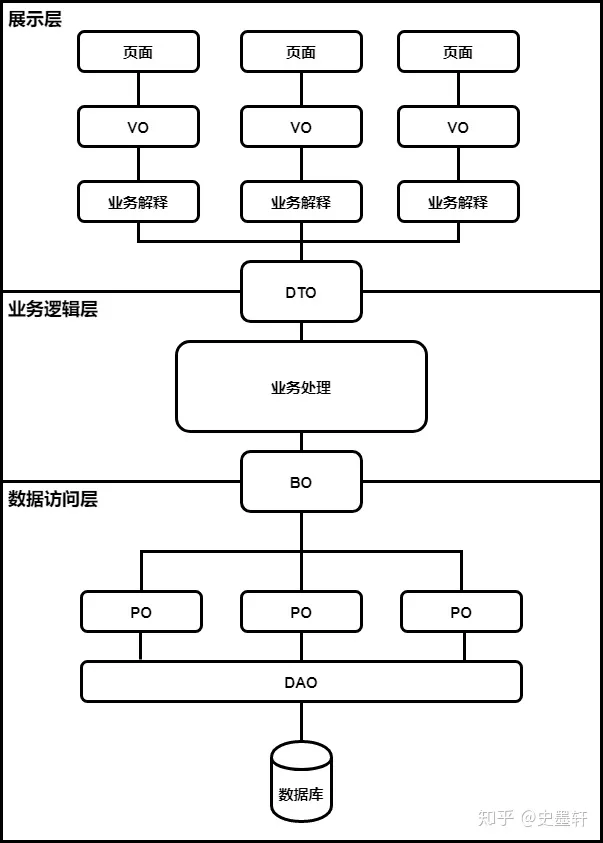
MyBatis入门
介绍
什么是MyBatis
MyBatis是一款优秀的持久层(Dao)框架,用于简化JDBC开发
MyBatis本是Apache的一个开源项目iBatis,2010年这个项目由apache software foundation迁移到了google code,并且改名为MyBatis。2013年11月迁移到Github
MyBatis 优点
如何写
Mapper代理开发
定义与SQL映射文件同名的Mapper接口,并且将Mapper接口和SQL映射文件放置在同一目录下

设置SQL映射文件的namespace属性为Mapper接口全限定名

在Mapper接口中定义方法,方法名就是SQL映射文件中sql语句的id,并保持参数类型和返回值类型一致

编码
- 通过SqlSession的getMapper方法获取Mapper接口的代理对象
- 调用对应方法完成sq的执行

细节:如果Mapper接口名称和SQL映射文件名称相同,并在同一目录下,则可以使用包扫描的方式简化SQL映射文件的加载

配置讲解
MyBatis核心配置文件的顶层结构如下:

编写配置文件时,需要遵守标签的顺序规则,按上面的来顺序不能乱
类型别名(typeAliases)
类型别名可为 Java 类型设置一个缩写名字。 它仅用于 XML 配置,意在降低冗余的全限定类名书写。例如:
1 | <!--指定一个包名,MyBatis 会在包名下面搜索需要的 Java Bean--> |
Mapper语法编写
XML 映射器官方详细文档。MyBatis 的真正强大在于它的语句映射,这是它的魔力所在。
编写流程
编写接口方法:Mapper接口
参数:增删改查所需的参数
结果:有返回值:
List、实体类,无返回值:void
编写SQL语句:XML映射文件
执行方法,测试
namespace
语法空间:关联对应的mapper类

resultMap
resultMap 元素是 MyBatis 中最重要最强大的元素。官方文档详解
数据库的字段名称 和 实体类的属性名称 不一样,则不能自动封装数据
起别名:用as 对不一样的列名,让别名和实体类的属性名一样
缺点:每次查询都要定义一次别名1
2
3select
id, brand_name as brandName, company_name as companyName, ordered, description, status
from tb_brand;使用sql片段 缺点:每次查询不同的列名都要重写,不灵活
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9<sql id="brand_column">
id, brand_name as brandName, company_name as companyName, ordered, description, status
</sql>
<select id="selectAll" resultType="brand">
select
<include refid="brand_column"></include>
from tb_brand;
</select>resultMap:
定义
<resultMap>标签在
<select>标签中,使用resultMap属性替换 resultType属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16<!--resultMap
id:唯一标识
type:映射的类型,支持别名
-->
<resultMap id="brandResultMap" type="brand">
<!--id的写法:<id column="id" property="id"/>-->
<!--普通列的写法↓-->
<result column="brand_name" property="brandName"/>
<result column="company_name" property="companyName"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectAll" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select
*
from tb_brand;
</select>
SQL语句块
sql语句块包含了以下常见的语法:
insert– 映射插入语句。update– 映射更新语句。delete– 映射删除语句。select– 映射查询语句。
1 | <!-- |
语句块里sql语句常见的一些写法说明:
1 | <!-- |
多条件查询
需求分析
查询多个条件:
- 当前状态:精确查询
status = ? - 企业名称:模糊查询
company_name like ? - 品牌名称:模糊查询
brand_name like ? - 同时成立 => 使用and连接

三种查询方式
分析完需求后,编写xml映射(以下三种查询方式都是统一的xml配置)
1 | <select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap"> |
散装参数查询
@Param("XXX")指定xml接受的名称1
2
3
4
5// Mapper接口定义
List<Brand> selectByCondition(int status, String companyName, String brandName);
// 调用查询
List<Brand> brands = selectByCondition(status, companyName, brandName);实体类封装对象查询
只需要保证SQL中的参数名和实体类属性名对应上,即可设置成功
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10// Mapper接口定义
List<Brand> selectByCondition(Brand brand);
// 封装对象
Brand brand = new Brand();
brand.setStatus(status);
brand.setBrandName(brandName);
brand.setCompanyName(companyName);
// 调用查询
List<Brand> brands = brandMapper.selectByCondition(brand);Map集合查询
只需要保证SQL中的参数名和Map集合的键的名称对应上,即可设置成功
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10// Mapper接口定义
List<Brand> selectByCondition(Map map);
// 封装对象
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("status", String.valueOf(status));
map.put("companyName", companyName);
map.put("brandName", brandName);
// 调用查询
List<Brand> brands = brandMapper.selectByCondition(map);
动态查询
当条件为可选的时候,SQL语句需要随着用户的输入或外部条件的变化而变化,MyBatis提供了**动态查询**功能
- if:条件判断
- choose(when, otherwise):多个条件中选择一个使用
- trim(where ,set):帮忙删掉额外的东西
- foreach:循环遍历
if
当前端页面为多个参数组合时,且不确定参数具体有几个,可以选择if
1 | <select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap"> |
注意:
- if 判断公式的连接使用
and或者or,而不是&& - 用
<where>标签代替手写的where,<where>会自动删除SQL语句里多余的and
choose
当前端页面只传来一个参数,且不确定是哪个参数,可以选择choose
1 | <select id="selectByConditionSingle" resultMap="brandResultMap"> |
注意:
<choose>标签和<where>一起用嗷- 有
<where>标签情况,<otherwise>里假如为空且前面判断都不成立,则后面自动加上where id < 1(查不出数据)
添加数据
1 | <insert id="add" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"> |
注意:
事务提交:写完添加、修改、删除语句后需要
commit才会更改到数据库
主键返回:在数据添加成功后,需要获取插入数据库数据的主键的值

- useGeneratedKeys:默认false,设置为ture后就会返回
keyProperty所设置的键值 - keyProperty:要返回的主键,一般是id
- useGeneratedKeys:默认false,设置为ture后就会返回
更新数据
用Update更新数据库字段,主要注意点就是
- 可以用
<set>和<if>标签编写动态SQL - 记得commit
1 | <update id="update"> |
1 |
|
批量删除
foreach
foreach对集合进行遍历,其属性有:
- collection:迭代的对象,默认为
array,可以在maaper接口里使用@Param注解改变Map集合的默认key的名称 - item:单次迭代获取到的值
- index:单次迭代获取到的索引
- separator:迭代之间的分隔符
- open、close:指定开头与结尾的字符串
- nullable:可否为空
示例代码
编写一个Mapper接口,注意这里的@Param注解:可以改变collection的默认的名称
1 | /** |
编写XML映射文件
1 | <!-- |
编写执行方法
1 | //1. 获取SqlSessionFactory... |
MyBatis参数传递
MyBatis提供了ParamNameResolver类来进行参数封装

MyBatis注解开发
使用注解开发会比配置文件开发更加方便
1 |
|
- 查询:@Select
- 添加:@Insert
- 修改:@Update
- 删除:@Delete